ISRO pushing Venus mission Shukrayaan to 2031 (GS Paper 3, Science and Tech)
Why in news?
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is yet to receive approval from the Indian government for the Venus mission and that the mission could as a result be postponed to 2031.
Background:
- ISRO’s Venus mission, called Shukrayaan I, was expected to be launched in December 2024.
- The idea was born in 2012; five years later, ISRO commenced preliminary studies after the Department of Space received a 23% hike in the 2017-2018 budget.
- The organisation sought payload proposals from research institutes in April 2017.
- Optimal launch windows from Earth to Venus occur once around every 19 months. This is why ISRO has ‘backup’ launch dates in 2026 and 2028 should it miss the 2024 opportunity.
Other missions to Venus:
- But even more optimal windows, which further reduce the amount of fuel required at liftoff, come around every eight years.
- Both the U.S. and the European space agencies have Venus missions planned for 2031 referring to VERITAS and EnVision, respectively while China might go anytime: 2026, 2027, whenever they want to go.
Shukrayaan I:
- ISRO had originally hoped to launch Shukrayaan I in mid-2023 but cited the pandemic when it pushed the date to December 2024. Other ISRO missions, including Aditya L1 and Chandrayaan III, have also been affected by manufacturing delays and commercial launch commitments.
- Shukrayaan I will be an orbiter mission. Its scientific payloads currently include a high-resolution synthetic aperture radar and a ground-penetrating radar.
- The mission is expected to study Venus’s geological and volcanic activity, emissions on the ground, wind speed, cloud cover, and other planetary characteristics from an elliptical orbit.
Budget:
- ISRO received an allocation of ₹13,700 crore in the 2022-2023 budget, marginally higher than the year before. The bulk was diverted to the human spaceflight mission, Gaganyaan.
- Ahead of the forthcoming budget announcement, and following recent reforms in the private spaceflight sector, various industry groups have drafted a wishlist, including boosts to local manufacturing and procurement.
Musk's SpaceX launches secret satellite for US Space Force, land twin rockets
(GS Paper 3, Science and Tech)
Why in news?
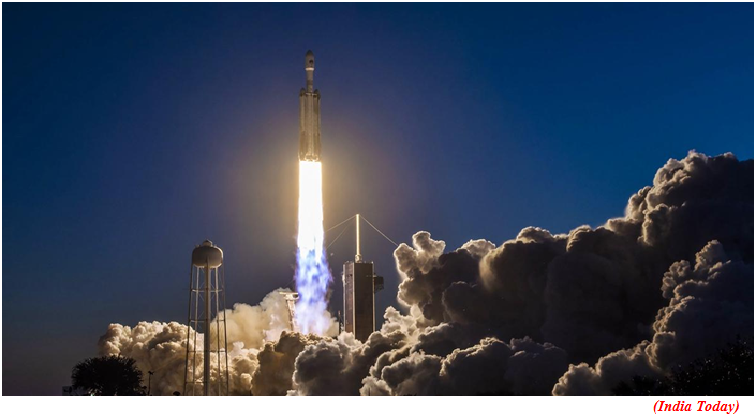
- In what was the first Falcon-Heavy launch of the year, Elon Musk's SpaceX launched a classified mission for the United States Space Force (USSF) from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida.
The mission also carried the Long Duration Propulsive ESPA (LDPE)-3A payload adapter that can hold up to six small satellites and five of those slots were filled on the mission.

CBAS-2:
- The primary satellite for the mission was Continuous Broadcast Augmenting SATCOM 2 (CBAS-2) which was sent into geostationary orbit over 35,000 kilometers above Earth.
- The satellite provides communications relay capabilities in support of our senior leaders and combatant commanders.
- The mission of CBAS-2 is to augment existing military satellite communication capabilities and continuously broadcast military data through space-based satellite relay links.
Flacon-Heavy:
- The Flacon-Heavy is the most powerful rocket built by the company that is propelled by three modified first stages of the Falcon-9 rocket. The three boosters are strapped together with the central booster pushing the payload into the designated orbit around the planet.
- So far, the Falcon-Heavy has conducted five launches and a total of 11 landings.
- As one of the world’s most powerful operational rockets, Falcon Heavy can lift nearly 64 metric tons to orbit.
- The rocket is powered by 27 Merlin engines that together generate more than 5 million pounds of thrust at liftoff, equal to approximately eighteen 747 aircraft.



