Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre gets new trisonic wind tunnel (GS Paper 3, Science and Tech)
Why in news?
- Recently, the new trisonic wind tunnel at the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC) was inaugurated by conducting the first blow-down test successfully.
- The massive structure, which can perform tests in three speed regimes, equips the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) with a robust in-house support system for space missions.
What are wind tunnels?
- Wind tunnels are devices used to study the effects of air flows on solid objects; in this case, scale models of ISRO rockets and spacecraft.
Trisonic wind tunnel:
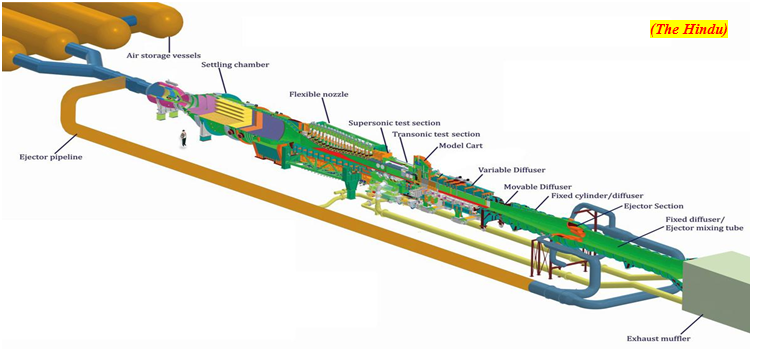
- The Trisonic Wind Tunnel is a system to aid aerodynamic design of rockets and re-entry spacecrafts by characterizing a scaled model by evaluating forces, moments, load distribution, unsteady pressures, acoustic levels etc.
- The tunnel has an overall length of about 160m and has a maximum cross section of 5.4m.
- The tunnel can be used for testing various space vehicles in three flight regimes - below the speed of sound, at the speed of sound and above the speed of sound: hence the name trisonic wind tunnel.
- The tunnel can simulate flight conditions from 0.2 times the speed of sound (68 m/s) to 4 times the speed of sound (1360 m/s).
What is blow down test?
- In a ‘blow down test’, stored gases are released and blown through the tunnel’s test section, simulating flight conditions.
- The tunnel can simulate flight conditions from 0.2 times the speed of sound to four times the speed of sound, according to the space agency.
Way Forward:
- It is a big step towards self-reliance in the aerospace sector by India.
Centre introduces Bills to modify ST list in four States
(GS Paper 2, Governance)
Why in news?
- Recently, the government introduced four Bills that seek to modify the Scheduled Tribes (ST) list in the four States of Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Himachal Pradesh and Chhattisgarh in Lok Sabha, via amendments proposed in the Constitution (Scheduled Tribes) Order, 1950.
- Union Minister of Tribal Affairs introduced these Bills in the Lok Sabha.
Key Highlights:
- The Bill seeks to add the Narikoravan and Kuruvikkaran hill tribes to the ST list of Tamil Nadu.
- The demand for their inclusion dates to before 1965 and even the Lokur Committee had in its report of that year recommended its inclusion.
- The government also moved a bill to introduce Betta-Kuruba as a synonym for the already categorised Kadu kuruba in the ST list of Karnataka.
- It also moved a bill to add a number of synonyms in Devanagri script for the already categorised BhariyaBhumia tribe in the ST list of Chhattisgarh.
- They are all part of the same tribe but had been kept out of the list just because they pronounced and spelt their names differently.
- The Hattee community of Trans-Giri region in Sirmaur district was added to the ST list of Himachal Pradesh—a demand pending for almost five decades.

Way Forward:
- From time to time, the government brings such bills to give effect to modifications proposed by various states in relation to the ST list.
ILO declaration urges countries to ensure labour protection
(GS Paper 2, International Organisation)
Why in news?
- Recently, the17th Asia and the Pacific Regional Meeting (APRM) of the International Labour Organization (ILO) concluded with governments, workers’ and employers’ organizations agreeing to bolster efforts to achieve social justice and decent work for all.
- It set ten-point priorities of national action for the member countries to deal with the issue of dwindling wages of workers, inflation and unemployment.

Key Highlights of Singapore Declaration:
- The “Singapore Declaration”, agreed that social dialogue was essential to address labour market challenges and finding solutions in crisis situations.
- It urged the governments to ensure labour protection for all through the promotion of freedom of association and the effective recognition of the right to collective bargaining throughout the regions, including for workers in vulnerable situations and workers in the informal economy, as enabling rights for decent work.
- It called for closing gender gaps in the world of work through measures that increase women’s labour force participation, promote equal pay for work of equal value, balance work and responsibilities, and promoting women’s leadership.
- The declaration also urged the governments to strengthen governance frameworks and respect for freedom of association to protect the rights of migrant workers.
About ILO:
- It is the only tripartite U.N. agency, since 1919. It brings together governments, employers and workers of 187 member States.
- Established as an agency for the League of Nations following World War I by the Treaty of Versailles in 1919.
- It became the first specialised agency of the United Nations (UN) in the year 1946.
- It got the Nobel Peace Prize in 1969.
- Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland.




