Extreme heat waves may break human survivability limit in India World Bank (GS Paper 2, International Organisation)

Why in news?
- Recently, the World Bank releases a report titled “Climate Investment Opportunities in India's Cooling Sector”.
- As per this report, extreme heat waves are increasing with alarming frequency across India in the past few decades and soon the country may become one of the first places in the world to experience heat waves that break the human survivability limit.
Extreme temperature:
- The severe heat waves are responsible for thousands of deaths across the country, where higher temperatures are arriving early and staying for far longer periods.
- In April 2022, India was plunged into the grip of a punishing early spring heat wave that brought the country to a standstill, with temperatures in the capital, New Delhi, topping 46 degrees Celsius. The month of March, which witnessed extraordinary spikes in temperatures, was the hottest ever recorded.
Economic impact:
- The rising heat across India can hit economic productivity, observing that 75 per cent of India's workforce or 380 million people depend on heat-exposed labour, at times working in potentially life-threatening temperatures.
- By 2030, India may account for 34 million of the projected 80 million global job losses from heat stress associated productivity decline.
- The lost labour from rising heat and humidity could put up to 4.5 per cent of India's GDP at risk by the end of this decade.
One District One Product (ODOP) initiative operationally merged with Districts as Export Hub (DEH) initiative
(GS Paper 2, Governance)
Why in news?
- ODOP initiative is operationally merged with ‘Districts as Export Hub (DEH)’ initiative of the DGFT, Department of Commerce, with the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) as a major stakeholder.
ODOP Initiative:
- Central Government has initiated One District One Product (ODOP) in all States/UTs of the country, as a transformational step towards realizing the true potential of a district, fueling economic growth, generating employment and rural entrepreneurship, taking us to the goal of Aatmanirbhar Bharat.
- The ODOP Initiative is aimed at fostering balanced regional development across all districts of the country, enabling holistic socio-economic growth across all regions.
- The objective is to focus on District of the country as unit for converting into a manufacturing and export hub by identifying products with export potential in the District.
- The Department is engaging with State and Central Government agencies to promote the initiative of ODOP, which is an on-going process.
 initiative.png)
Districts Export Action Plans:
- In this context, Districts Export Action Plans include specific actions required to support local exporters / manufacturers in producing / manufacturing identified products in adequate quantity and with the requisite quality, for reaching potential buyers outside India, thereby creating economic value.
- These plans also include identifying and addressing challenges for exports of such identified products/services, improving supply chains, market accessibility and handholding for increasing exports, paving way for employment generation.
The following are some of the achievements of ODOP:-
- The ODOP GeM Bazaar was launched on the Government e-Marketplace (GeM) on 29th August 2022 with over 200 product categories created on the platform to promote sales and procurement of ODOP products across the country.
- The ODOP initiative has been identified for the prestigious Prime Minister’s Award for Excellence in Public Administration in Holistic Development through One District One Product (ODOP) category in April, 2022.
India takes another big step towards achieving 500 GW of non-fossil fuel based electricity installed capacity by 2030
(GS Paper 3, Environment)
Why in news?
- Recently, the Union Minister for Power and NRE launched the plan “Transmission System for Integration of over 500 GW RE Capacity by 2030".
High-level committee:
- Ministry of Power had constituted a high-level committee under Chairperson, Central Electricity Authority with representatives from Solar Energy Corporation of India, Central Transmission Utility of India Ltd, Power Grid Corporation of India Ltd, National Institute of Solar Energy, and National Institute of Wind Energy for planning the transmission system required for having 500 GW of non-fossil fuel based installed capacity by 2030.
- The Committee prepared a detailed Plan titled “Transmission System for Integration of over 500 GW RE Capacity by 2030" in consultation with States and other stakeholders.
Key Highlights:
- The Plan is a major step towards achievement of the goal of integrating 500 GW of non-fossil fuel based capacity by 2030 by providing broad plan of required transmission system for having 537 GW of Renewable Energy capacity by the year 2030.
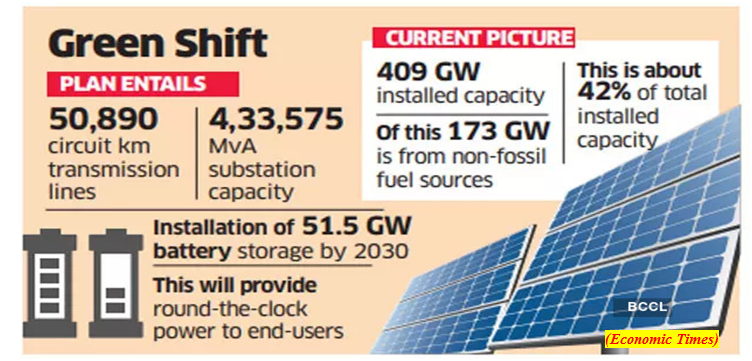
- The planned additional transmission systems required for having 500 GW of non-fossil fuel include 8120 ckm of High Voltage Direct Current Transmission corridors (+800 kV and +350 kV), 25,960 ckm of 765 kV ac lines, 15,758 ckm of 400 kV lines and 1052 ckm of 220 kV cable at an estimated cost of 2.44 lakh crore.
- The transmission plan also includes transmission system required for evacuation of 10 GW off-shore wind located in Gujarat and Tamilnadu at an estimated cost of Rs. 0.28 lakh crore. With the planned transmission system, the inter-regional capacity will increase to about 1.50 lakh MW by 2030 from 1.12 lakh MW at present.
- Considering the availability of Renewable Energy based generation for a limited period during day, the Plan also envisages installation of Battery Energy Storage Capacity of the order of 51.5 GW by 2030 to provide Round the Clock power to end-consumers.
Potential generation centres:
- The Plan has identified major upcoming non-fossil fuel based generation centres in the country, which include Fatehgarh, Bhadla, Bikaner in Rajasthan, Khavda in Gujarat, Anantapur, Kurnool RE Zones in Andhra Pradesh, offshore wind potentials in Tamil Nadu and Gujarat, RE park in Ladakh etc. and based on these potential generation centres, transmission systems have been planned.
- The planned transmission system projected will provide a visibility to the Renewable Energy Developers about the potential generation sites and scale of investment opportunity.
Way Forward:
- India has huge ambitions in energy transition and plans to have 500 GW of non-fossil fuel based electricity installed capacity by 2030, so that cleaner fuel comprises of 50% of the installed capacity mix by 2030.
- The installed electricity generating capacity in the country at present is 409 GW comprising of 173 GW from non-fossil fuel sources, which is about 42% of the total installed electricity generating capacity.
- For evacuation of power from the planned Renewable capacity by 2030, a robust transmission system needs to be in place in advance as the gestation period of wind and solar based generation projects is much less than that of associated transmission system.



 initiative.png)
