Regulation of satellites in Low Earth Orbit (LEO) (GS Paper 3, Science and Tech)
Context:
- The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the United States will vote on major issues of space debris as more and more satellites reach Low Earth Orbit, congesting the already tightened space above Earth.
- The organisation will aim to introduce new rules to address the growing risks of orbital debris.
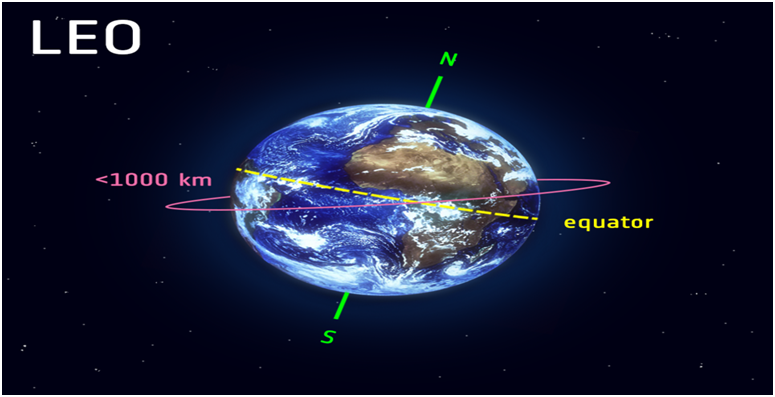
What is LEO?
- The Low Earth Orbit is normally at an altitude of less than 1000 kilometers but could be as low as 160 kilometers above Earth.
- The American agency, FCC currently regulates operators of satellites in LEO to ensure spacecraft will re-enter Earth’s atmosphere within 25 years following the completion of missions.
Key Highlights:
- The new FCC rules could reduce the timeframe that is required to maintain satellites in orbit once their missions are complete, after which they have to re-enter into Earth's atmosphere for a fiery demise.
- The new rules will be an update to the 2004 regulations calling for satellite post-mission disposal as soon as practicable but no more than five years.
- The new rules would apply to both US-licensed satellites and systems, and non-US satellites seeking US market access.
Challenges of space debris:
- Defunct satellites, discarded rocket cores, and other debris now fill the space environment, creating challenges for future missions, there were 4,800 satellites currently operating in orbit.
- As the number of objects in space increases, so too does the probability of collisions. At risk is more than the $279 billion-a-year satellite and launch industries and the jobs that depend on them.
- It also endangers satellite connectivity that is critical to modern life, including broadband in remote areas, navigation, and video.
Way Forward:
- With small satellites and constellations being launched by companies like SpaceX, OneWeb and others, there is a growing demand from global countries to enhance space monitoring and tracking in order to safeguard space assets from collisions in Low Earth Orbit.
Indian Navy launches third stealth frigate 'Taragiri' under Project 17A
(GS Paper 3, Defence)
Why in news?
- ‘Taragiri’, the third stealth frigate of the Indian Navy's Project 17A, was launched in Mumbai recently.
- This ship has been built using an integrated construction methodology which involves hull block construction in different geographical locations and integration and erection on the slipway at the Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders (MDL).

Salient features:
- Vessel has an approximate launch weight of 3,510 tons
- The vessel is being launched with an approximate launch weight of 3,510 tons.
- The frigate is designed by the Indian Navy’s in-house design organization, the Bureau of Naval Design.
Project 17A:
- The first ship of Project 17A, ‘Nilgiri’, was launched on 28 September, 2019, and is expected for sea trials in the first half of 2024.
- The second ship of the ‘Udaygiri’ class under the project was launched on 17 May, 2022. It is expected to start sea trials during the second half of 2024.
- The keel of the fourth and final ship was laid on 28 June.
Way Forward:
- The keel of ‘Taragiri’ was laid on 10 September, 2020. The ship is expected to be delivered by August 2025.
China discovers a new mineral on the moon
(GS Paper 3, Science and Tech)
Why in news?
- Recently, China announced the name of the new mineral as Changesite-(Y).
- It was found in rock and dust samples retrieved from the moon by China’s Chang’e-5 mission.
- The mission was launched in 2020 and was China's first to return a lunar sample.
Details:
- China has become only the third country to discover a new mineral on the moon.
- U.S. and Russia are the other two countries to have done so till date.
- It is the sixth new mineral humans have discovered on the moon.
Changesite-(Y):
- A research team from the Beijing Research Institute of Uranium Geology carefully separated a single crystalline particle of the material from more than 140,000 lunar particles using hi-tech processes, including X-ray diffraction.
- The particle was about 10 microns in diameter, or about one-tenth of a human hair.
- Changesite-(Y) is a phosphate mineral found in lunar basalts.

Phosphate:
- Phosphate is the natural source of phosphorous and is also found on Earth.
- It is an element that provides a major chunk of the nutrients plants need for their growth.
- While excess of it is damaging to the human body, it would play a key role in helping space faring heroes farm on the lunar surface.
Way Forward:
- The discovery of Changesite-(Y) was a breakthrough in mineralogy research and will help understand the history and evolution of the moon, besides helping with deep space exploration.
NCERT issues guidelines to schools for early identification of mental health problems in students
(GS Paper 2, Issues related to development of Social Sectors)
Why in news?
- The guidelines for ‘Early identification and intervention for mental health problems in school going children and adolescents’ have been released by the National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) following a mental health survey among school children.
- The survey report launched cited exams, results and peer pressure among major factors for stress and anxiety among school students.
Key Highlights:
- Setting up of a mental health advisory panel, school based mental health programme and pedagogical support to ensure mental well- being of students and engaging parents are among the guidelines issued by NCERT for schools.
- The schools should have a provision for identifying behaviour, substance use and self-harm, depression, and developmental concerns, provide first aid and make appropriate referrals.
- Most of the time mental health issues emerge at an early stage of life as half of all mental health conditions emerge by the time individuals are 14 years old and three-quarters by the age of 25, NCERT has recommended that apart from families and parents, teachers need to be informed about early flag signs as they too are the primary caregivers.

Mental health advisory panel:
- According to the manual, every school or groups of schools should establish a mental health advisory panel.
- It should be chaired by the principal and have teachers, parents, students and alumni as members.
- It will create awareness, and also plan and enforce an age and gender appropriate annual school mental health programme.
Training of teachers:
- Teachers must be trained in identifying early signs in students for attachment issues, separation anxiety, school refusal, communication issues, anxiety patterns, depressive states, conduct related issues, excessive internet use, hyperactivity, intellectual disability, and learning disabilities.
- Teachers should talk about bullying cases in class and empower students by educating them regarding bullying.
- They should provide a confidential way for students to report any incident which is of concern to them.
Why focus is on schools?
- Schools generally are seen as spaces where communities of learners have been expected to develop in a safe and secure environment. School management, principal, teachers, other staff, and students all spend around 1/3 of a day and around 220 days in a year in schools across the states and UTs in India.
For residential schools, the time spent by a student in the school community is even more. Therefore, it is the school's responsibility to ensure the safety, security, health, and well-being of all children in schools and hostels.





