Molecular mechanism behind intriguing green alga surviving in extreme conditions (GS Paper 3, Environment)
Why in news?
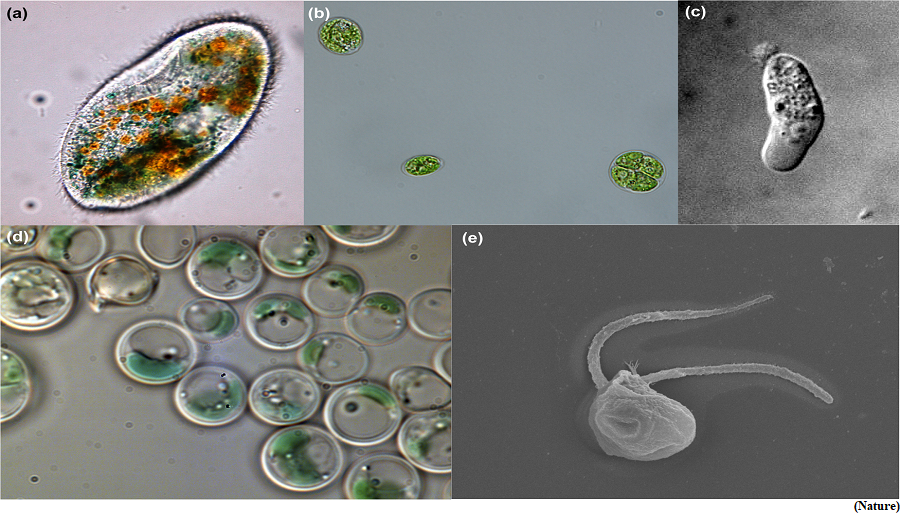
- A young researcher has divulged the secret of how one of the smallest green algae called Picocystis Salinarum survives the harshest of conditions by resorting to physiological adaptation to highly saline-alkaline/hyperosmotic conditions.
- This may pave the way for a promising future candidate for biotechnological applications like microalgal bioproducts and increasing salt tolerance in plants.
Carbonates:
- Carbonates are of great interest to geoscientists, biologists, and climatologists due to their significance in the global carbon cycle.
- The process of biologically converting inorganic carbon into organic carbon, known as carbon fixation, is widely recognized as the paramount biogeochemical transformation on our planet.
Background:
- What intrigued the Faculty from the Department of Earth Sciences, Pondicherry University was the mystery behind the capability of one organism called P. salinarum found in hypersaline soda lake Sambhar, Rajasthan, to survive extreme environments.
- Though the alga had been widely found in saline-soda lakes around the world, it was spotted for the first time in India only in the Sambhar Lake.
Key Highlights:
- They probed the molecular mechanisms of adaptation in such polyextreme conditions. This they carried out through studying the changes in protein abundances through a high-throughput label-free quantitation based quantitative proteomics method.
- They provided the first insights into the proteome of extremophilic alga P. salinarum revealing its tailored regulatory mechanisms for osmotic adaptation and proliferation in polyextreme conditions in soda lakes unraveling the basis of resilience in this not so known organism.
- The unique organism apparently enhances photosynthesis and ATP synthesis along with chaperone proteins as key response to high salinity-alkalinity.
- Enhanced photosynthetic activity exhibited by P. salinarum in highly saline-alkaline condition is noteworthy as photosynthesis is suppressed under hyperosmotic conditions in most photosynthetic organisms.
Way Forward:
- This discovery positions P. salinarum as a promising candidate for biotechnological applications and as a model organism for deciphering the molecular mechanisms of osmotic adaptation.
- They harnessed the unique characteristics of this microalga for bicarbonate-based integrated carbon capture and biomass production.
Parliamentary panel on criminal law Bill leaves decision on death penalty to Centre
(GS Paper 2, Governance)
Why in news?
- The proposed Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS) Bill, 2023, which seeks to replace the British-era Indian Penal Code (IPC), has increased the number of crimes which can attract the death penalty from 11 to 15, says a parliamentary panel report.

Abolition of the death penalty:
- India has in the past voted against a United Nations General Assembly’s draft resolution on the abolition of the death penalty.
- A study conducted by the National Law University, Delhi, the Annual Statistics Report 2022, published by Project 39A shows that till December 31, 2022, as many as 539 prisoners had been on death row in India, the highest since at least 2016.
- The parliamentary panel, headed by BJP member Brij Lal, recommended that the matter be left to the Union government to consider.
Dissent notes:
- Three Opposition members; P. Chidambaram and Digvijaya Singh of the Congress and Derek O’Brien of the Trinamool Congress submitted dissent notes against the provision.
- Mr. Singh said while the government had hailed the Bills as a move towards shedding the colonial nature of criminal laws, the Bills still retained the colonial spirit of the current laws and punishments for some offences had been made harsher and the death penalty had been added for at least four new crimes such as mob lynching, organised crime, terrorism and rape of a minor.
- According to the data, the Supreme Court has affirmed the death penalty in only seven cases in the last six years. While the imposition of the penalty itself causes distress and trauma, the wait before the sentence is set aside or confirmed causes distress many times more. It has been established that death penalty is no deterrent to serious crime.
- Mr. O’Brien, the Trinamool leader, said that based on national statistics, it can be observed that 74.1% of individuals on death row in India come from economically disadvantaged backgrounds.
Rarest of rare case:
- The domain experts submitted before the committee that the “rarest of rare case” doctrine should be defined in more objective terms, if the death penalty has to be retained.
- On the lines of ‘Sentencing Councils’ in the United Kingdom, the experts opined that the quasi-judicial boards should be made to exercise probation, commutation and remission to provide greater scope for victims to have a say; and timelines should be indicated for mercy petitions to be heard and disposed of.



