Plastic Rain (GS Paper 23, Science and Tech)

Why in news?
- Recently, a new study has found that around 74 metric tons of microplastics fell from the sky in New Zealand’s Auckland city in 2020.
- The study says this amount of microplastic is equivalent to 3 million plastic bottles.
- Researchers believe the prevalence of plastic rain is undercounted globally.
What is plastic rain?
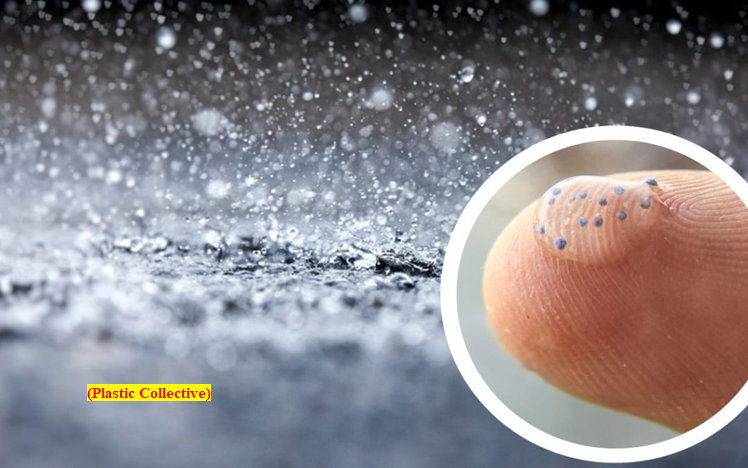
- Microplastics, very tiny pieces of plastic waste, less than 5 millimetres long, are raining from the sky.
- This microplastic emanates from packaging, clothing, vehicles, paint, worn car tyres and other sources.
- These small plastic particles are “flowing into the oceans via wastewater and tainting deep-sea ecosystems, and they’re even ejecting out of the water and blowing onto land in sea breezes”.
New study:
- The study conducted by the University of Auckland in New Zealand suggests that an average of around 5,000 pieces of microplastic fall on every square metre of Auckland’s urban rooftops any given day.
- During the experiment, the researchers caught the residue of eight types of airborne plastics from both sites.
- In Auckland, polyethylene, often used in packaging materials was the most-detected substance, followed by polycarbonate, a type of plastic typically used in electrical and electronic applications.
- On the days when strong winds from the coast gushed through the city, there was a rise in microplastics collected using a funnel and jar contraption.
- The production of airborne microplastics from breaking waves could be a key part of the global transport of microplastics.
Previous studies:
- In 2020, researchers found that 1,000 metric tons of microplastic particles enter 11 protected areas in the western United States every year – an equivalent of 120 million plastic water bottles.
- Another study, conducted in 2019 by scientists at Kings College London, said that an estimated average of 771 microplastic particles was found in central London.
- The rate of deposition of microplastic in London was much higher in London than in China’s Dongguan, China, Paris in France and Germany’s Hamburg.
- The study also highlighted sources of microplastic in the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean.
Health effects:
- Earlier, a study revealed that people inhale up to 7,000 airborne microplastic particles every day.
- This was “100 times higher than expected” and can pose a “potential health threat that could rank alongside asbestos or tobacco”.
- In March 2022, scientists announced microplastics were detected flowing through human veins.
- The microplastic can potentially cause “inflammation and stress to cells”.
Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Ko Kaam Karyakram (PMKKK) now named as Pradhan Mantri Virasat Ka Samvardhan (PM VIKAS) Scheme
(GS Paper 2, Governance)
Why in news?
- Recently, the Union Minister of Minority Affairs, in a written reply to a question in the Lok Sabha informed that the Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Ko Kaam Karyakram (PMKKK) has now been named as Pradhan Mantri Virasat Ka Samvardhan (PM VIKAS) Scheme.
- The integrated scheme converges five erstwhile schemes of the Ministry viz.
- Seekho aur Kamao,
- USTTAD,
- Hamari Dharohar,
- Nai Roshni and
- Nai Manzil.

Key Highlights:
- The scheme has been approved by the Cabinet for the period of 15th Finance Commission.
- PM VIKAS aims to improve livelihoods of the minorities, particularly the artisan communities, using the components of skill development, education, women leadership & entrepreneurship.
- These components compliment each other in the ultimate objective of the scheme to increase the incomes of the beneficiaries and provide support by facilitating credit and market linkages.
Priority sectors:
- The priority sectors under PMJVK are education, health, skill development, women centric projects etc.
- In North Eastern Region (NER), the States of Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim and Tripura are covered under PMJVK.
Implementation:
- The proposals under PMJVK are sent by the States/Union Territories (UTs) as per demand for infrastructure in the identified areas, which are considered and approved by the Empowered Committee (EC) of PMJVK, after due consultation with the concerned Central Ministries.
- Projects under PMJVK are implemented and managed by the concerned State/ UT Government.
- PMJVK is a demand driven scheme and State/ UT-wise allocation of funds is not made under the scheme.
5th edition of Youth Co:Lab for Young Entrepreneurs
(GS Paper 3, Economy)
Why in news?
- Recently, the 5th edition of Youth Co:Lab, Asia Pacific’s largest youth innovation movement was jointly launched by Atal Innovation Mission (AIM), NITI Aayog and UNDP India.
Youth Co:Lab
- Youth Co:Lab is an initiative launched in 2019 by UNDP India in partnership with Atal Innovation Mission, NITI Aayog.
- It aims to establish a common agenda for Asia-Pacific countries to invest in and empower youth to accelerate implementation of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) through leadership, social innovation, and entrepreneurship.

Significance:
- Atal Innovation Mission, along with UNDP India are driving this movement through the fifth edition of Youth Co:Lab India and have been supporting young social entrepreneurs who can be a powerful force in leading social change and furthering the implementation of SDGs target actions.
- The Youth Co:Lab initiative, till date, has been implemented in 28 countries and territories, reaching over 200,000 participants, benefitting more than 11,000 young social entrepreneurs and supporting over 1,240 social enterprises.
Focus thematic areas:
- Through Youth Co: Lab, 30 early-stage start-ups would be supported by the springboard programme, and the best would be provided a seed grant for scaling up their start-up. The 5 focus thematic areas for Youth Colab 2022-23 are:
- Digital and Financial Literacy for Youth
- Gender Equality and Women Economic Empowerment
- Developing FinTech Solutions focused on Biodiversity Conservation
- Promoting Biodiversity-friendly Lifestyles through Technological Solutions in Finance
- Accelerating Circular Economy through Upcycling Innovations
- Behavioural Nudges for LiFE ( Lifestyle For Environment)
About Atal Innovation Mission (AIM):
- AIM is the Government of India’s endeavor to promote a culture of innovation and entrepreneurship.
- Its objective is to serve as a platform for the promotion of world-class innovation hubs, grand challenges, start-up businesses, and other self-employment activities, particularly in technology-driven areas.
China builds ropeway, roads near tri-junction
(GS Paper 2, International Relation)
Why in news?
- China has set up a ropeway near the Torsa Nala on its side of the India-Bhutan-China tri-junction, and is strengthening roads and other infrastructure along the entire eastern sector.
Yangtse area:
- In the Yangtse area of Tawang sector, which saw a scuffle recently, China had stepped up patrols some years ago to assert its claims in the area.
- The Chinese usually patrol two to three times a year, before and after winter and there are four major ingress points in the Yangtse area which the PLA uses to enter the region.
- Yangtse is located 30-35 km northeast of Tawang and is at an altitude of around 17,000 feet.
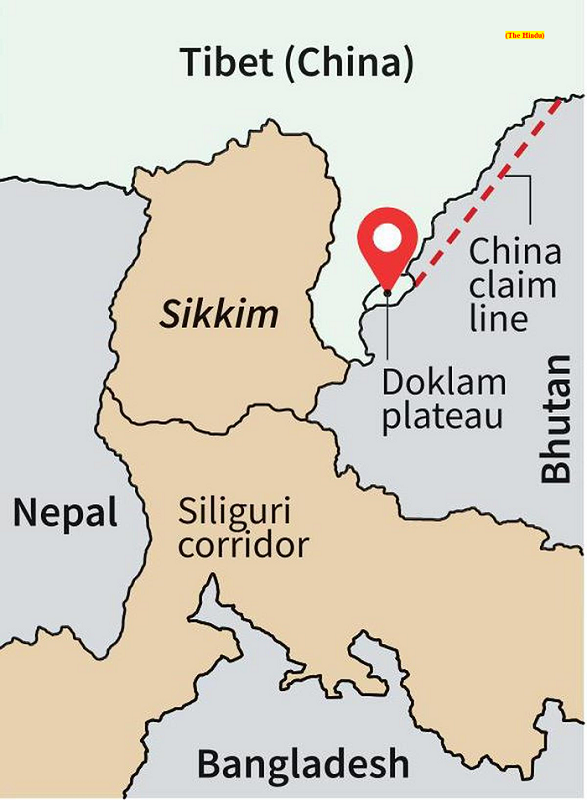
Construction near Torsa Nala:
- The People’s Liberation Army (PLA) has installed a ropeway close to the Torsa Nala on their side near the confluence point, and some new anchor points of the ropeway have been recently observed.
- There is also lot of activity near the Torsa Nala near Doklam, a location that saw a 73-day standoff between Indian and Chinese forces a few years ago.
Line of Actual Control (LAC):
- The Line of Actual Control (LAC) is divided into the western (Ladakh), middle (Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand), and eastern (Arunachal Pradesh and Sikkim) sectors.
- India has also been significantly upgrading its infrastructure along the LAC in the last few years, with further ramping-up post the 2020 standoff in Galwan in eastern Ladakh.
- In 2021, China and Bhutan reached an agreement on a 3-step roadmap to resolve their boundary issues, including the Doklam area, after 24 rounds of negotiations that began in 1984.
Recent conflict:
- The Army’s statement giving details of the scuffle between Indian and Chinese troops on December 9 noted that, in certain areas along the LAC in the Tawang sector, there are areas of differing perception, where both sides patrol the area upto their claim lines. This has been the trend since 2006.
- India and China have mutually agreed disputed areas and areas of differing perception along the 3,488 km-long LAC.
- For instance in eastern Ladakh, there are two mutually agreed disputed areas, Trig Heights and Demchok, while there are 10 areas of differing perception. Similarly, Yangtse is one of the eight major friction points in the eastern sector.





