Competency Model for Civil Servants (GS Paper 4, Ethics)
Context
- The Capacity Building Commission (CBC) of India has introduced the Karmayogi Competency Model as part of its ongoing efforts to enhance the skills and capabilities of civil servants.
- This initiative represents a fundamental shift in how civil service functions, aiming to transform individuals from mere employees (karmachari) into committed and effective workers (karmayogi).
- This model emphasizes the importance of not just performing tasks, but embodying the ethos of dedicated public service.
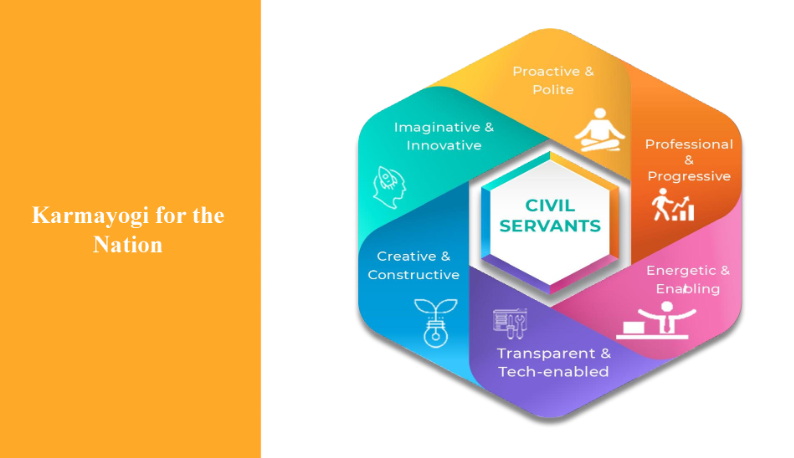
Overview of the Karmayogi Competency Model
- The Karmayogi Competency Model serves as a structured framework that identifies essential competencies required for civil servants.
- It focuses on aligning the skills of civil servants with their roles and responsibilities, ensuring that they are adequately trained to meet the challenges of governance.
- This alignment is facilitated through training courses available on the Integrated Government Online Training (iGOT) portal, which enhances accessibility and relevance.
Components of the Competency Model
The competency model is divided into two main categories: Behavioral Competencies and Functional Competencies.
- Behavioral Competencies:
- This category encompasses 13 competencies, which are crucial for personal and professional development. These competencies are further divided into:
- Core Competencies: Essential attributes that every civil servant should possess.
- Leadership Competencies: Skills that enhance the ability to lead and inspire others.
- Key behavioral competencies include:
- Self-awareness: Understanding one’s strengths and weaknesses to improve performance.
- Personal effectiveness: Skills related to time management, decision-making, and productivity.
- Creativity and innovation: The ability to think outside the box and develop new solutions.
- Strategic leadership: Skills necessary to lead teams and projects effectively.
- These competencies are inspired by four guiding principles that all public officials should embody:
- Vikas (Development): Commitment to promoting growth and progress in society.
- Garva (Pride): Fostering a sense of pride in public service and its impact.
- Kartavya (Duty): Upholding the responsibilities and ethical obligations of public service.
- Ekta (Unity): Promoting harmony and collaboration within the civil service and society at large.
- Functional Competencies:
- This category consists of 21 competencies specifically tailored to the skills required for various roles in governance. These competencies ensure that civil servants are equipped to perform their functions effectively.
- Key functional competencies include:
- Citizen-centricity: Placing citizens at the heart of governance and service delivery.
- Policy architecture: Skills necessary for designing and implementing effective policies.
- Digital fluency: Proficiency in using digital tools and technologies for governance.
- Financial management: Skills related to budgeting, financial planning, and resource allocation.
- Data analytics: The ability to analyze and interpret data to inform decision-making.
Mission Karmayogi National Program
Mission Karmayogi was launched in 2020 as a flagship initiative of the Government of India aimed at revolutionizing civil service training. The mission seeks to transition the functioning of civil services from a "Rule Based" approach to a more flexible "Role Based" and citizen-centric model. It is structured around six foundational pillars:
- Policy Framework: Establishing guidelines and principles to steer capacity-building initiatives in civil service.
- Institutional Framework: Developing institutions that support the training and development of civil servants.
- Competency Framework: Aligning training and development programs with the competencies outlined in the Karmayogi Competency Model.
- Digital Learning Framework: Leveraging digital platforms, particularly the iGOT-Karmayogi platform, to deliver training.
- Electronic Human Resource Management System (e-HRMS): Implementing a digital system for managing human resources within the civil service.
- Monitoring and Evaluation Framework: Establishing metrics to assess the effectiveness and impact of capacity-building programs.
Key Features of Mission Karmayogi
- Capacity Building Commission (CBC): Established in April 2021, the CBC plays a crucial role in overseeing the implementation of capacity-building initiatives. It ensures that programs align with the objectives of Mission Karmayogi. The commission includes diverse representation from the private sector and civil society, enhancing its effectiveness.
- iGOT Platform: The Integrated Government Online Training (iGOT) platform is a cornerstone of Mission Karmayogi. It provides civil servants with access to training resources anytime, anywhere, using any device. This flexibility allows for personalized learning experiences tailored to individual roles and skill gaps. The platform is designed to support approximately 20 million users, significantly expanding the reach of training programs.
- Annual Capacity Building Plans (ACBP): Each government department is required to create and implement its own capacity-building plan. These plans are aligned with departmental priorities and objectives, ensuring that training is relevant and targeted.
- Role-based Competency Framework: Training programs are specifically designed to develop the competencies needed for each civil servant's role, ensuring that the skills learned are applicable and useful in their daily responsibilities.
Integrated Government Online Training (iGOT) Portal
The iGOT portal is a vital part of the Digital India initiative, aiming to modernize the training of government employees. Key features include:
- Accessible Learning: The portal enables "anytime, anywhere, any device" learning, breaking the barriers of traditional training methods. Civil servants can engage in self-paced learning, making it easier to balance training with their responsibilities.
- Marketplace for Training Content: The platform is envisioned to evolve into a vibrant marketplace for educational content. Government ministries can curate and share training materials, supported by a robust e-learning content industry. This collaborative approach ensures that the training remains up-to-date and relevant.
- Scalability: The initiative aims to reach around 20 million government employees, which was previously unattainable through conventional training methods. This scalability is crucial for building a competent civil service workforce.
Conclusion
- Mission Karmayogi represents a transformative approach to civil service training in India, focusing on developing a workforce that is not only skilled but also deeply committed to serving the public.
- By embedding the principles of citizen-centric governance and leveraging technology for continuous learning, the program aims to equip civil servants with the necessary tools to meet contemporary challenges.
- The successful implementation of this competency model and the associated training initiatives will significantly contribute to the development of a Viksit Bharat (Developed India) by 2047.
- By nurturing a new generation of tech-savvy, effective Karmayogis, India can ensure that its civil service is well-prepared to drive national progress and enhance public welfare.
- This initiative not only seeks to improve individual competencies but also aims to foster a culture of excellence and accountability within the civil service, ultimately benefiting the citizens they serve.


