Turkmenistan-Afghanistan-Pakistan-India Pipeline (GS Paper 2, IR)
Introduction
- The Turkmenistan-Afghanistan-Pakistan-India (TAPI) pipeline, a major USD 10 billion infrastructure project, is poised to reshape energy dynamics and foster regional cooperation.
- After prolonged delays, primarily due to security concerns in Afghanistan, work on the TAPI pipeline is set to begin, promising enhanced energy connectivity and economic development for the region.
What is the TAPI Pipeline?
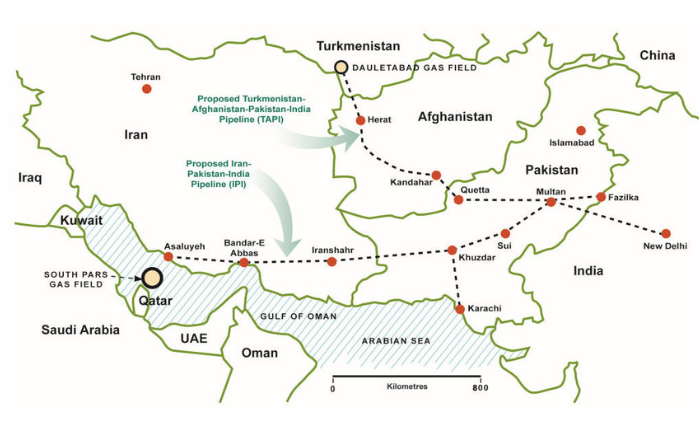
- The TAPI pipeline is designed to transport natural gas from Turkmenistan’s Galkynysh gas field through Afghanistan, Pakistan, and India.
- Spanning approximately 1,814 kilometers, the pipeline is expected to deliver around 33 billion cubic meters (BCM) of natural gas annually.
- The distribution of gas will be allocated as follows: Afghanistan (5%), Pakistan (47.5%), and India (47.5%) over its 30-year operational life.
- Often referred to as the ‘Peace Pipeline,’ TAPI aims to promote regional cooperation and stability.
- The project’s development began in the 1990s, with significant progress achieved in 2003 and India joining the initiative in 2008.
- The TAPI Pipeline Company Limited (TPCL), a joint venture among the four participating countries, will oversee the pipeline’s construction and operation.
Significance of the TAPI Pipeline
Environmental Impact:
- Cleaner Energy Transition: The TAPI pipeline offers a vital alternative to coal, significantly reducing carbon emissions. For India, which heavily relies on coal, this project supports a transition to cleaner energy and helps meet its Net-Zero Emissions Target.
- Reduction in Air Pollution: By providing a cleaner energy source, the pipeline could alleviate air pollution in major cities such as Delhi, Mumbai, Karachi, and Islamabad.
Economic Benefits:
- Economic Growth: The pipeline promises economic benefits, including job creation and revenue from transit fees, particularly for Afghanistan and Pakistan. It could also stimulate investment in renewable energy within these countries.
- Investment Opportunities: The project could serve as a catalyst for economic development, potentially attracting further investments in regional infrastructure.
Strategic Influence:
- Geopolitical Dynamics: TAPI plays a strategic role in the regional geopolitical landscape, countering the Iran-Pakistan-India (IPI) pipeline supported by Iran and Russia. For Turkmenistan, it offers a chance to diversify its export markets beyond existing routes to China and Russia.
- Balancing Chinese Influence: With China’s investment in the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC), TAPI could act as a counterbalance to Chinese influence, particularly in Pakistan.
Regional Cooperation:
- Enhanced Connectivity: The pipeline aims to strengthen connections among Central and South Asian countries, fostering cooperation in energy, transportation, and communication sectors.
- Strategic Partnerships: For India, TAPI is integral to improving energy security and connectivity with Central Asia, aligning with its broader regional strategy.
Challenges Facing the TAPI Pipeline
Security Concerns:
- Instability in Afghanistan: The pipeline will traverse Afghanistan, a region with significant political instability and security challenges, potentially jeopardizing the project’s implementation.
Financing and Administration:
- Funding Hurdles: Securing adequate funding remains a challenge. While the Asian Development Bank (ADB) will contribute, substantial funding must come from private investors.
- Complex Administration: The involvement of four countries introduces administrative complexities, requiring effective coordination among the participating nations.
Investment Climate:
- Economic Barriers: Turkmenistan’s closed economy and governance issues present obstacles to attracting international investment. Corruption and regulatory challenges further complicate the investment landscape.
Political Tensions:
- India-Pakistan Relations: Ongoing political tensions between India and Pakistan could impact the pipeline’s long-term viability and smooth operation.
Environmental Considerations:
- Impact of Natural Gas: While cleaner than coal, natural gas extraction and transportation pose environmental risks, including potential water and soil pollution.
India’s Regional Strategy
- Securing Trade Routes: Central Asia’s strategic location is crucial for India’s trade and energy security. Strengthening ties with Central Asian nations aligns with India’s economic and strategic interests.
- Economic Engagement: The Chabahar Port Agreement with Iran and negotiations with the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) highlight India’s efforts to enhance regional connectivity and trade.
- Military and Security Initiatives: India’s military presence in Tajikistan and joint exercises with Uzbekistan underscore its commitment to regional security and defense partnerships.
- Geopolitical Challenges: China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) and strained relations with neighboring countries necessitate strategic maneuvering to secure India’s position in Central Asia.
Way Forward
To ensure the success of the TAPI pipeline, several measures are recommended:
- Diversify Funding Sources: Explore private sector investments, international financial institutions, and government grants to secure necessary funding.
- Incentivize Investment: Offer tax breaks, subsidies, and a stable regulatory environment to attract foreign investors.
- Promote Industrial Development: Develop infrastructure along the pipeline route to stimulate economic activity and create jobs.
- Enhance Security Cooperation: Strengthen regional security frameworks to safeguard the pipeline and ensure its operational continuity.
- Engage Local Communities: Foster positive relations with communities along the pipeline route to mitigate security risks and gain local support.
- Adopt Best Environmental Practices: Implement measures to minimize the environmental impact of natural gas extraction and transportation.
The TAPI pipeline represents a significant opportunity for regional integration and energy cooperation, despite the challenges. By addressing these challenges effectively, the project can contribute to economic growth and stability in the region while advancing India’s strategic interests.


