Abhay Mudra in Buddhism (GS Paper 1, Indian Literature)
Introduction
- Mudras, the ritualistic hand gestures used in Indian spiritual practices, carry deep symbolic meanings and are integral to the iconography of various religions.
- Among these, the Abhay Mudra stands out for its profound message of fearlessness and protection.
- This mudra is not only a crucial element in Buddhist teachings but also resonates across different cultural and religious contexts.
- Recently, the political invocation of the Abhay Mudra in India has brought renewed attention to its significance and symbolism.
Context
- The Leader of the Opposition in the Indian Parliament invoked the image of Lord Shiva and the Abhay Mudra during a parliamentary speech.
- This gesture was used to criticize the government's perceived threats to the constitution and the idea of India.
- By employing this symbolic gesture, the leader sought to convey a message of resistance, protection, and fearlessness against such perceived threats.
Role of Leader of Opposition in Lok Sabha
- The Leader of the Opposition (LoP) in the Lok Sabha (LS) plays a pivotal role in the Indian parliamentary system.
- This position is held by the leader of the largest opposition party, provided the party has at least one-tenth of the total seats in the Lok Sabha.
- The LoP is integral to various parliamentary committees and selection panels for key statutory positions, providing necessary checks and balances to government policies and decisions.
- While the position is not constitutionally mandated, it was given statutory recognition in 1977, highlighting its importance in a functioning democracy.
Understanding Abhay Mudra
- Mudras: Mudras are symbolic hand gestures used in various Indian spiritual practices, including yoga, meditation, and dance. These gestures are believed to influence the flow of prana (vital energy) within the body and are used to convey specific meanings, emotions, and spiritual concepts.
- Abhay Mudra: The Abhay Mudra, or the "gesture of fearlessness," is a prominent mudra in Buddhist and Hindu iconography. It is depicted with the right hand raised to shoulder height, palm facing outward, and fingers pointing upwards. This gesture symbolizes protection, reassurance, and the dispelling of fear.
- Origin: The Abhay Mudra is traditionally associated with the Buddha immediately after his enlightenment. It represents the moment when the Buddha tamed a mad elephant, illustrating his ability to provide fearlessness and protection to his followers. This mudra symbolizes security, serenity, and compassion emanating from enlightenment.
- Association with Other Religions: The Abhay Mudra is also found in other religious traditions, including Christianity and Jainism, where it similarly symbolizes protection and fearlessness.
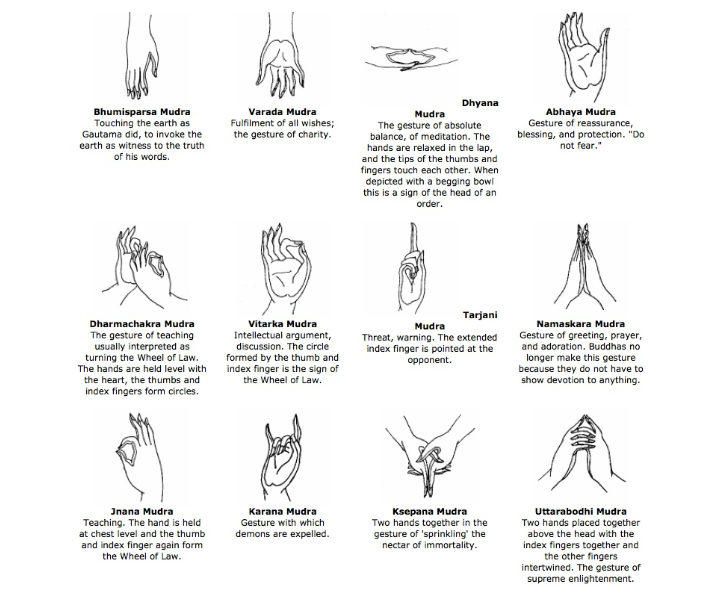
Other Types of Mudras in Buddhism
DharmaChakra Mudra:
- Description: Hands held in front of the chest with the thumb and index finger forming a circle, representing the wheel of Dharma.
- Significance: Symbolizes the Buddha's first sermon after enlightenment, representing the initiation of teaching Dharma and the constant cycle of birth, death, and rebirth.
Bhumisparsha Mudra:
- Description: Right hand touching the ground, left hand resting on the lap.
- Significance: Represents the Buddha's enlightenment and the earth witnessing his attainment of enlightenment, symbolizing overcoming obstacles through meditation.
Varada Mudra:
- Description: Right hand extended downward, palm facing outward.
- Significance: Symbolizes generosity and the five perfections: generosity, morality, patience, effort, and meditative concentration.
Dhyana Mudra:
- Description: Hands placed on the lap, right hand on top of the left, thumbs touching.
- Significance: Represents meditation, concentration, and inner peace.
Anjali Mudra:
- Description: Palms pressed together in front of the chest.
- Significance: Represents respect, greeting, and gratitude, similar to Namaskara or Namaste.
Vitarka Mudra:
- Description: Right hand up, thumb and index finger forming a circle.
- Significance: Symbolizes the transmission of knowledge and the communication of the Buddha's teachings.
Uttarabodhi Mudra:
- Description: Hands in front of the chest, left fingers pointing upward, right fingers pointing downward, thumbs together forming a triangle.
- Significance: Represents the union of wisdom and compassion and the attainment of enlightenment.
Karana Mudra:
- Description: Left hand at the heart, palm facing forward, index and little fingers pointing up.
- Significance: Symbolizes protection and the dispelling of negativity.
Jnana Mudra:
- Description: Index finger and thumb together forming a circle, other fingers extended.
- Significance: Represents the unity of individual consciousness with universal consciousness.
Tarjani Mudra:
- Description: Index finger extended upward, other fingers curled.
- Significance: Known as the "threatening gesture," used as a symbol of warning or protection against evil forces.
Conclusion
- The Abhay Mudra, like other mudras in Buddhism, holds profound spiritual and cultural significance.
- It symbolizes fearlessness, protection, and the compassionate guidance of the enlightened Buddha.
- The recent political reference to the Abhay Mudra in India underscores its enduring relevance and powerful symbolism.
- In a broader context, mudras like Abhay serve as timeless symbols of spiritual ideals, guiding individuals towards inner peace and resilience.
- As we navigate contemporary challenges, these ancient gestures continue to inspire and remind us of the universal quest for fearlessness and protection.


