Addressing Plant Nutrient Imbalance: The Imperative of Balanced Fertilisation (GS Paper 3, Environment)
Why in News?
- Post the Lok Sabha polls, the government is poised to prioritize capping the consumption of urea and DAP to rectify worsening plant nutrient imbalances.
Need for Balanced Fertilisation:
- Overutilization: India has witnessed a surge in fertilizer use, particularly urea, with consumption increasing by 16.9% from 2013-14 to 2024.
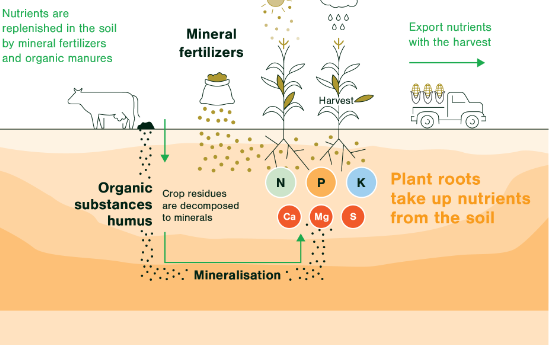
- Imbalance in Usage: The ratio of NPK (Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium) usage has become skewed, with excessive nitrogen (N) use, leading to reduced efficiency and environmental concerns.
- Challenges with Nutrient Based Subsidy (NBS): While NBS aimed at promoting balanced fertilization, it inadvertently led to imbalances due to urea's exclusion and recent price controls on non-urea fertilizers.
Initiatives and Concerns:
- Success of Neem-Coated Urea: Neem-coated urea improved nitrogen use efficiency; however, urea consumption persists despite regulations.
- Import Dependency and Price Volatility: India's reliance on imports exposes it to price fluctuations, impacting foreign exchange and subsidy burden.
- Opportunity Amidst Price Drops: Cooling international prices offer a window for the government to rationalize prices and adjust subsidy rates.
Nutrient Based Subsidy Scheme:
- Aim: Introduced in 2010 to promote balanced fertilization and agricultural productivity.
- Coverage: Provides subsidies for non-urea-based fertilizers based on their nutrient content, administered by the Department of Fertilizer.
- Objectives: Encourage balanced fertilizer use, reduce subsidy burden, improve availability, and foster competition among fertilizer companies.
Future Directions:
- Establishing Price Hierarchy: Adjusting prices to reflect nutrient content can incentivize balanced fertilization, promoting optimal usage.
- Promoting Complex Fertilizers: Encouraging the use of complex fertilizers tailored for diverse crops and soils can enhance nutrient profiles.
- Innovative Fertilizers: Exploring options like sulphur-coated urea for gradual nutrient release can optimize uptake and minimize environmental impact.
- Encouraging Sustainable Practices: Promoting sustainable fertilization practices can enhance crop yields, mitigate environmental risks, and bolster agricultural resilience.
Conclusion:
- Balanced fertilization is pivotal for sustainable agricultural growth.
- As the government deliberates on policy interventions post-elections, prioritizing balanced fertilization can foster efficient resource utilization, enhance agricultural productivity, and promote environmental sustainability in the long run.


