Bharat Ratna for Swaminathan, Rao, Charan Singh (GS Paper 2, Polity and Governance)

Why in news?
- The Bharat Ratna will be conferred on former Prime Ministers P.V. Narasimha Rao and Chaudhary Charan Singh, as well as Green Revolution pioneer M.S. Swaminathan, adding to the two awardees already announced earlier in 2024; socialist leader Karpoori Thakur, and former Deputy Prime Minister L.K. Advani.
Details:
- This year’s tally of five Bharat Ratna awardees, one more than the four announced in 1999, is the highest that has ever been announced in a single year.
- Four of the five awards announced this year are posthumous.
PV Narasimha Rao:
- Former Prime Minister PV Narasimha Rao was posthumously awarded the Bharat Ratna, India's highest civilian honour, for bringing economic reforms to India at a time when the country was grappling with both economic and political challenges.
- He served as the tenth prime minister of India from 1991 to 1996.
- He is credited for bringing many economic reforms in the country, particularly for dismantling the Licence Raj.
- When he became the PM, India's economic crisis was threatening the macro-economic stability of the country. His government immediately launched several economic reforms. It was during Rao's tenure that Manmohan Singh became the finance minister.
Dr. M.S. Swaminathan:
- Mankombu Sambasivan Swaminathan, born on August 7, 1925, dedicated his life to eradicating hunger and poverty.
- Despite initially pursuing a career in medicine, he was deeply moved by the Bengal famine of 1942-43, prompting him to switch his focus to agriculture.
- Working alongside Nobel laureate Norman Borlaug, Swaminathan spearheaded efforts to introduce high-yielding varieties of rice and wheat.
- The Green Revolution, characterized by the widespread adoption of modern agricultural techniques, drastically increased crop yields and transformed India's food production landscape.
- His contributions to agriculture and farmers' welfare earned him widespread acclaim. His visionary leadership and dedication to innovation earned him the title of "Father of the Green Revolution."
Chaudhary Charan Singh:
- Born in 1902 in Noorpur area of Meerut district in Uttar Pradesh, Charan Singh hailed from a middle-class peasant family.
- He was first elected to the Uttar Pradesh assembly in 1937 from Chhaprauli and represented the constituency in 1946, 1952, 1962 and 1967.
- He parted ways with the Congress in 1967 and became the Chief Minister of Uttar Pradesh for the first time, emerging as the leader of the Sanyukta Vidhayak Dal coalition. He was re-elected as chief minister for a second term in 1970.
- He was sworn in as the prime minister on July 28, 1979. But before he could prove his majority in the Lok Sabha, Indira Gandhi withdrew her party’s support to his government, leading to Singh’s resignation.
- He was the chief architect of land reforms in Uttar Pradesh and took a leading part in formulation and finalisation of the Department of Redemption Bill 1939, which brought great relief to rural debtors.
About Bharat Ratna:
- Bharat Ratna is the highest civilian award of the Republic of India.
- Instituted in 1954, the award is conferred in recognition of exceptional service/performance of the highest order, without distinction of race, occupation, position, or sex.
- The award was originally limited to achievements in the arts, literature, science, and public services. But in December 2011, the government expanded the criteria to include any field of human endeavour.
NASA launches Pace to study Earth's oceans, atmosphere as planet warms
(GS Paper 3, Science and Technology)
Why in news?
- Nasa's Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) mission soared into orbit aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from the Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida recently.
- The PACE mission is a step forward in the study of Earth's oceans, air quality, and climate change.
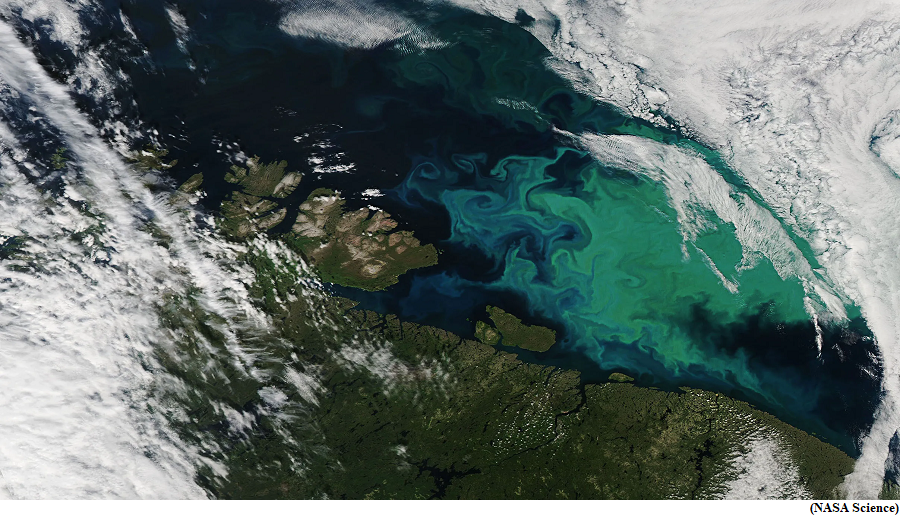
Instruments onboard:
- The satellite’s hyperspectral ocean color instrument will allow researchers to measure oceans and other waterbodies across a spectrum of ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared light.
- This will enable scientists to track the distribution of phytoplankton and identify which communities of these organisms are present on daily, global scales.
- Scientists and coastal resource managers can use the data to help forecast the health of fisheries, track harmful algal blooms, and identify changes in the marine environment.
- The spacecraft also carries two polarimeter instruments, Hyper-Angular Rainbow Polarimeter #2 and Spectro-polarimeter for Planetary Exploration.
- These will detect how sunlight interacts with particles in the atmosphere, giving researchers new information on atmospheric aerosols and cloud properties, as well as air quality at local, regional, and global scales.
- With the combination of the instrument and the polarimeters, PACE will provide insights into the interactions of the ocean and atmosphere, and how a changing climate affects these interactions.
Significance:
- Earth’s oceans are responding in many ways to climate change from sea level rise to marine heat waves to a loss of biodiversity.
- With PACE, researchers will be able to study climate change’s effects on phytoplankton, which play a key role in the global carbon cycle by absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and converting it into their cellular material.
- These tiny organisms drive larger aquatic and global ecosystems that provide critical resources for food security, recreation, and the economy.
- This data is vital for forecasting the health of fisheries, tracking harmful algal blooms, and detecting marine environmental changes.



