SUIT, the unique telescope to launch with Aditya L-1 mission (GS Paper 3, Science and Technology)
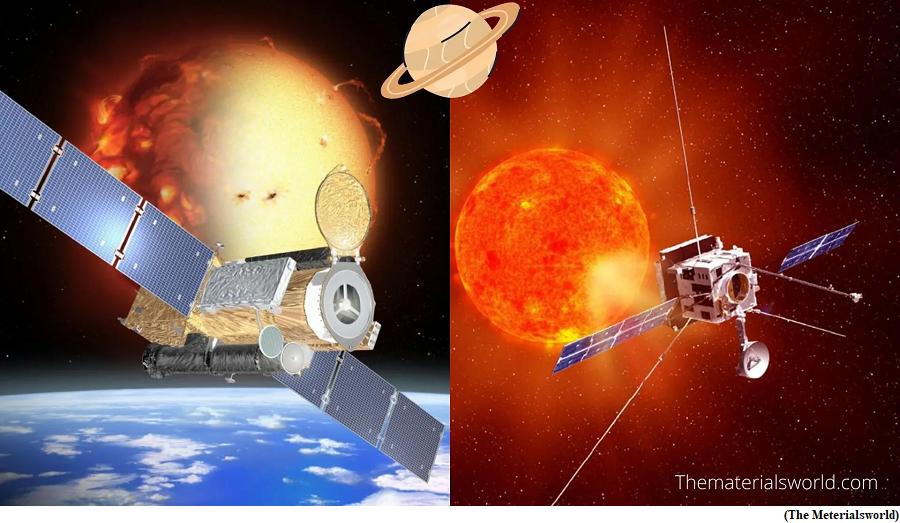
Why in news?
- Pune’s Inter-University Center for Astronomy and Astrophysics (IUCAA) has delivered the Solar Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (SUIT) to the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
- Suit will be launched onboard India's maiden mission to explore the Sun, Aditya L-1.
- It is one of the seven instruments being launched outside Earth with the mission to unravel the secrets of the Sun.
What is SUIT?
- The SUIT, designed by scientists at IUCAA, will study the Sun's ultraviolet (UV) emissions and capture high-resolution images of the Sun's atmosphere, known as the corona, in various UV wavelengths.
- The Sun is one of the most difficult things to study outside Earth due to its high emissions and radiation. With Aditya L-1, India wants to change that and see the star in our Solar System in a new light.
- SUIT will enable scientists to explore the dynamic and complex processes occurring in the Sun's outer layers.
Applications:
- Developed over a span of nearly a decade, SUIT will operate in the far and near ultraviolet regions, covering wavelengths of 200-400 nanometers.
- The instrument will observe the hotter and more dynamic regions of the Sun's atmosphere, such as the transition region and the corona.
- The chromosphere is the layer of the Sun's atmosphere that lies just above the photosphere. The corona is the outermost layer of the Sun's atmosphere.
- Once in space, it will also explore the dynamics of solar flares, sudden, violent outbursts of energy from the Sun.
- ISRO will use SUIT to monitor the Sun's activity and provide early warning of potential solar flares and CMEs, study the interaction between the Sun and the Earth's atmosphere, and try to better understand the role of the Sun in climate change.
VELC:
- ISRO had previously received the Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC) to be integrated with Aditya L-1 mission.
- VELC, developed primarily by IIA, will collect data for solving how the temperature of the corona can reach about a million degrees while the Sun’s surface itself stays just over 6,000 degrees Centigrade.
- The corona has so far only been studied during an eclipse when the disk is covered, and Aditya L-1 is aimed at better understanding the mechanism powering the Sun.
What is Aditya L-1 Mission?
- The Aditya L-1 mission is India's maiden mission to observe the Sun and is expected to launch by August this year.
- It will be launched nearly 1.5 million kilometers away from Earth to Lagrange Point 1 (L1), a stable point where the gravitational forces between the Earth and the Sun, as well as the centrifugal force of the rotating system, balance out.
- Out of the seven payloads, while four will directly view the Sun, three others will carry out in-situ studies of particles and fields at the Lagrange point L1.
Melting Hindu Kush Himalayas will decrease water in river basins by 2100, warns ICIMOD
(GS Paper 3, Environment)
Why in news?
- Recently, the Water, Ice, Society, and Ecosystems in the Hindu Kush Himalaya (HI-WISE) report from the International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) was relased.

Key Highlights:
- As Himalayan glaciers melt due to climate change, water availability in the Ganges, Indus and other river basins in the Hindu Kush region is set to increase in the short term and decrease in the long term.
- The contribution of water from glaciers will increase through 2050 and then decrease by 2100.
- As the glaciers continue to melt and get smaller, the water eventually starts to decrease. This point is called peak water, when the change occurs from increasing glacier runoff to decreasing glacier runoff.
- Many areas around the world have passed “peak water” and communities are dealing with less glacier meltwater.
Findings on Hindu Kush region:
- In the Hindu Kush region, melting snow and glaciers contribute significantly to river and groundwater flows. Rivers primarily get water from snowmelt in April-June and glacier melt during June-October. They also replenish aquifers.
- The Hindu Kush Himalayas have seen a 65 per cent faster loss of glacier mass. The glaciers lost a mass of 0.28 metres of water equivalent per year (m we) between 2010 and 2019, compared to 0.17 m we per year between 2000-2009.
Decline in snowfall:
- A decline in snowfall of 30–50 per cent is predicted to occur in the Indus Basin, 50–60 per cent in the Ganges, and 50-70 per cent in the Brahmaputra between 2070 and 2100 compared to the average snowfall between 1971 and 2000.
- As for snow, water runoff from this source has already fallen between 1979 and 2019 and is set to fall further, jeopardising the livelihoods of 129 million farmers in the Indus, Ganges and Brahmaputra basins. The number of days with snow cover has decreased by five days per decade.
- In the Brahmaputra River basin especially, the trend in snow cover area since 2002 shows a clear downward trend.
Impact on communities:
- The decreasing snow cover could dry up springs, which is bad for agriculture. Plants are now more directly exposed to the cold weather, when they could hide under a blanket of snow earlier.
- About 83 per cent of springs, the main source of water for mountain communities, are replenished through snowmelt and glacier melt. As the snow cover decreases, it will have dire consequences for the 240 million people living in the mountains.
- Variations in snow cover make it harder for mountain communities to adapt.
India to buy 31 Predator drones from US for $3.5 bn
(GS Paper 3, Defence)
Why in news?
- Recently, India's Defence Acquisition Council (DAC) approved the purchase of US-Made Predator drones.
- The deal will cost India around $3.5 billion for 31 high-altitude, long-endurance Predator-B drones.
- India already operates two Sea Guardian drones, an unarmed version of the deadly Predator series.
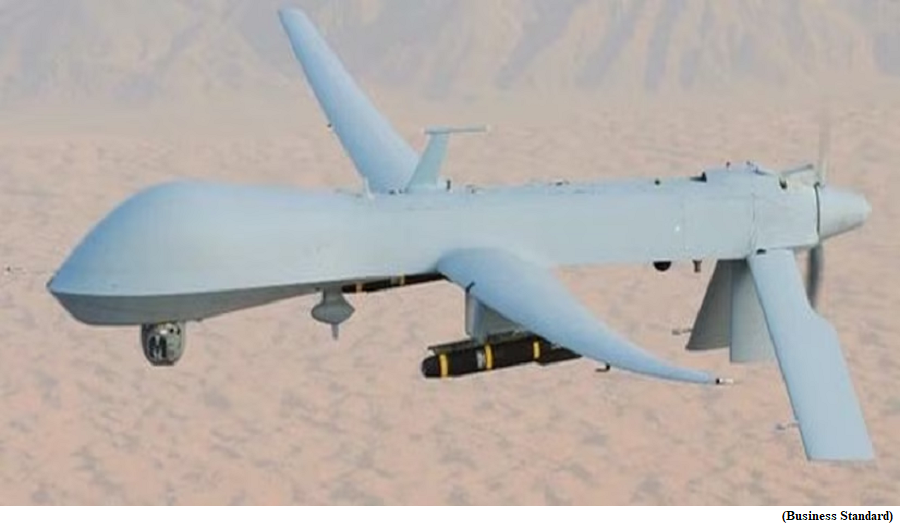

What are Predator Drones?
- Developed by a San Diego-based defence contractor, General Atomics, Predators drones are considered the best in the business.
- Primarily developed to conduct surveillance-related operations, one of these drones famously identified Osama bin Laden in Afghanistan in 2000.
- Thereafter, armed versions of the Predator drones were developed that came with lethal Hellfire missiles.
- These drones can operate at heights up to 50,000 feet for over 27 hours with a payload capacity of 1,746 kg.
- India is interested in the MQ-9B SkyGuardian and MQ-9B SeaGuardian variants of these drones, which are designed to operate via satellite and have endurance of more than 30-40 hours.
- These drones can fly in all weather conditions with payloads of more than 2000kg.
Predator drones operational history: A brief
- Since it started serving with the American armed forces in 1995, Predator drones have seen extensive usage in the conflict zone.
- The Predator was first deployed over Bosnia in the summer of 1995 and General Atomics was awarded the first contract of series production in August 1997.
- Later, it was deployed in Afghanistan, Iraq, Yemen, Libya, Somalia, and Syria to support operational requirements.
Where does India stand in the drone race?
- India is taking a keen interest in improving indigenous know-how of drone technology and its liberal policies and other initiatives like drone shakti are supporting the market's growth.
- Drone Shakti is a production-linked incentive scheme designed to bolster domestic drone development.
DRDO Rustom:
- The DRDO Rustom is a medium-altitude long-endurance unmanned air vehicle (UAV) being developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation. It has been derived from National Aerospace Laboratory (NAL's) LCRA (Light Canard Research Aircraft developed by the team that worked under the late Prof Rustom Damania in the 1980s.
Three variants:
- The Rustom will have three variants namely, Rustom-1, a tactical UAV with an endurance of 12 hours.
- The second is Rustom-H, a larger UAV with a flight endurance of more than 24 hours which will also have a higher range and service ceiling. Service ceiling refers to the maximum height an aerial vehicle can achieve.
- The third, Rustom-2 (TAPAS-BH-201) will be a UAV based on Rustom-H. It is being developed on the lines of General Atomics MQ-1 Predator. Its first flight took place in November 2016.




